Operating Principle of a Boiler
I./Operating Principle of a Boiler and Safety Measures
Operating Principle of a Boiler
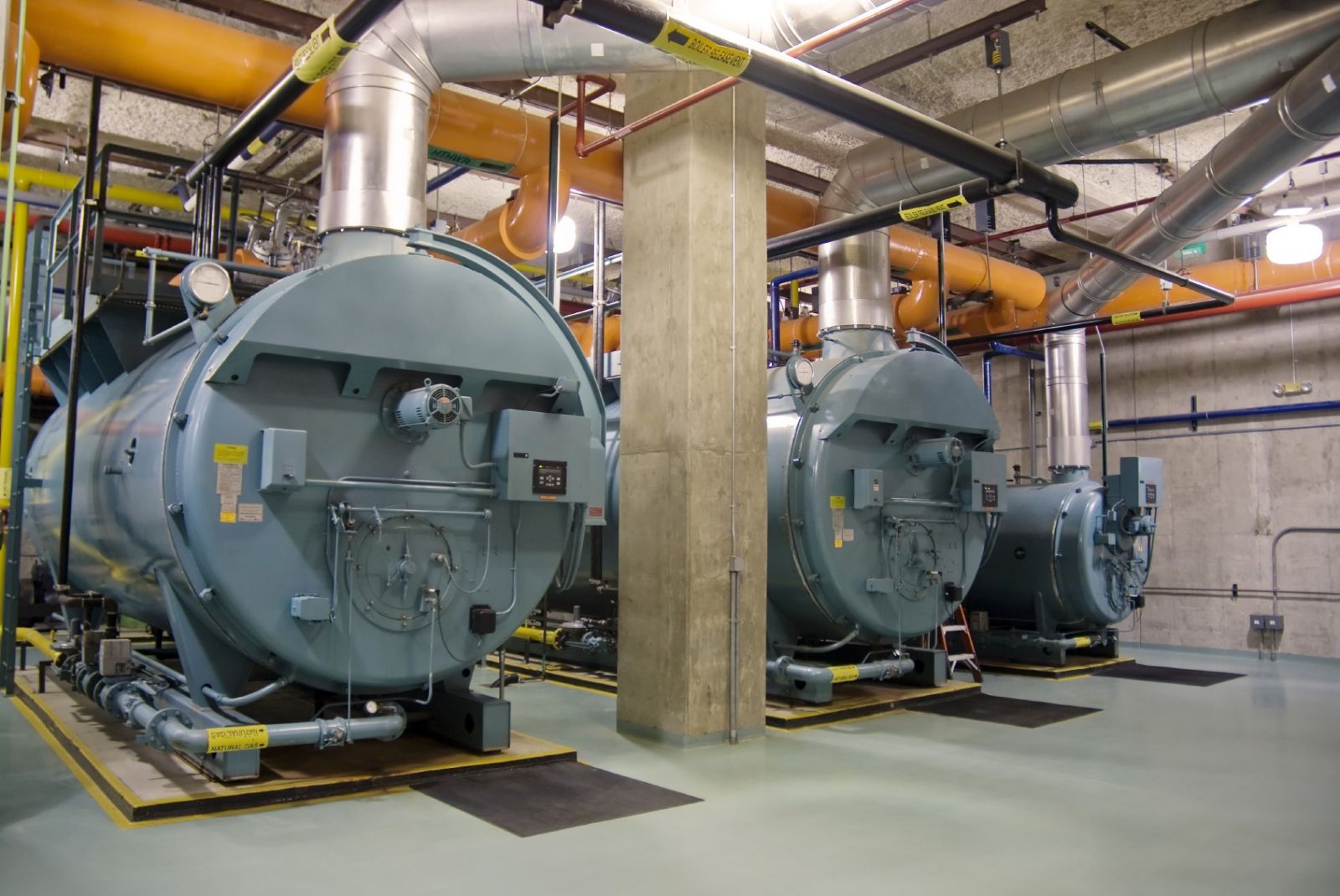
A boiler, also known as a steam generator, is a device that converts water into steam using heat generated from fuel combustion. This steam is then used for various industrial purposes such as heating, power generation, and running machinery. Below is a basic overview of how a boiler operates:
-
Fuel and Combustion System:
-
Fuel: Fuel, which can be coal, oil, gas, or biomass, is fed into the boiler's combustion chamber.
-
Combustion: The fuel is burned in the combustion chamber, generating heat. This process requires a supply of air or oxygen to sustain combustion.
-
-
Heat Transfer:
-
Direct Heat Transfer: The heat generated from combustion is directly transferred to water through the heat exchange surfaces of water tubes or steam pipes.
-
Convection and Radiation Heat Transfer: Heat is also transferred via radiation from the flame and convection from the combustion gases.
-
-
Water to Steam Conversion:
-
Water Reservoir: Water is stored in a reservoir and comes into contact with the heat exchange surfaces.
-
Boiling and Evaporation: As heat is transferred to the water, its temperature rises until it reaches the boiling point and begins to evaporate, producing high-pressure steam.
-
-
Steam Collection and Utilization:
-
Steam Collection: The generated steam is collected and directed through steam pipes to various systems for utilization.
-
Steam Use: The steam is used to generate mechanical power, heat, or electricity.

-
II/ Safety Measures for Boilers
Ensuring safety in boiler operation is crucial. Here are several safety measures to protect boiler operations:
-
Pressure Control Systems:
-
Safety Valves: Safety valves are installed to release excess pressure if it exceeds safe levels.
-
Pressure Gauges: These help monitor and ensure pressure remains within safe limits.
-
-
Temperature Control Systems:
-
Temperature Sensors: These monitor the water and steam temperature to ensure it does not exceed safe levels.
-
Thermostats: Automatically adjust the temperature to maintain safe operating conditions.
-
-
Water Level Control:
-
Water Level Alarms: Warn when the water level is too low or too high, preventing damage from water shortage or overflow.
-
Feed Water Controllers: Ensure a continuous and stable supply of water to the boiler.
-
-
Emergency Protection Systems:
-
Emergency Shut-off Systems: Allow immediate shutdown of the boiler in case of emergency.
-
Safety Switches: Automatically cut off power if any faults or hazards are detected.
-
-
Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
-
Routine Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the boiler to ensure all components function properly.
-
Comprehensive Inspections: Perform detailed inspections, including pressure testing, water quality testing, and safety device checks.
-
-
Training and Education of Personnel:
-
Safety Training: Ensure operators are thoroughly trained in safety procedures and boiler operation.
-
Ongoing Training: Provide regular updates and training sessions to keep personnel informed about the latest safety practices and technologies.
-
By implementing these measures, boiler operation becomes safer, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring efficient production while protecting the health and safety of workers.
Related News

Drifco – High-Quality Fire Protection Valves from China | Distributed by PME
13/03/2026
Drifco is a professional manufacturer specializing in fire protection valves and firefighting system equipment from China. With many years of experience in the fire protection industry, Drifco provides high-quality valve solutions widely used in automatic sprinkler systems, fire protection water supply systems, and industrial fire safety systems. Drifco products are manufactured under strict quality control processes and comply with international standards, ensuring durability, reliability, and stable performance under high pressure and demanding operating conditions.

General Principles for Selecting a Steam Trap
09/03/2026
Before selecting a steam trap, the following factors must be determined: Type of equipment or application: Heat exchanger, steam main, steam tracing, etc. Operating pressure and temperature: The steam trap must be able to withstand the corresponding pressure and temperature conditions. Condensate flow rate: The trap must be capable of discharging sufficient condensate to allow the equipment to operate at optimal efficiency.

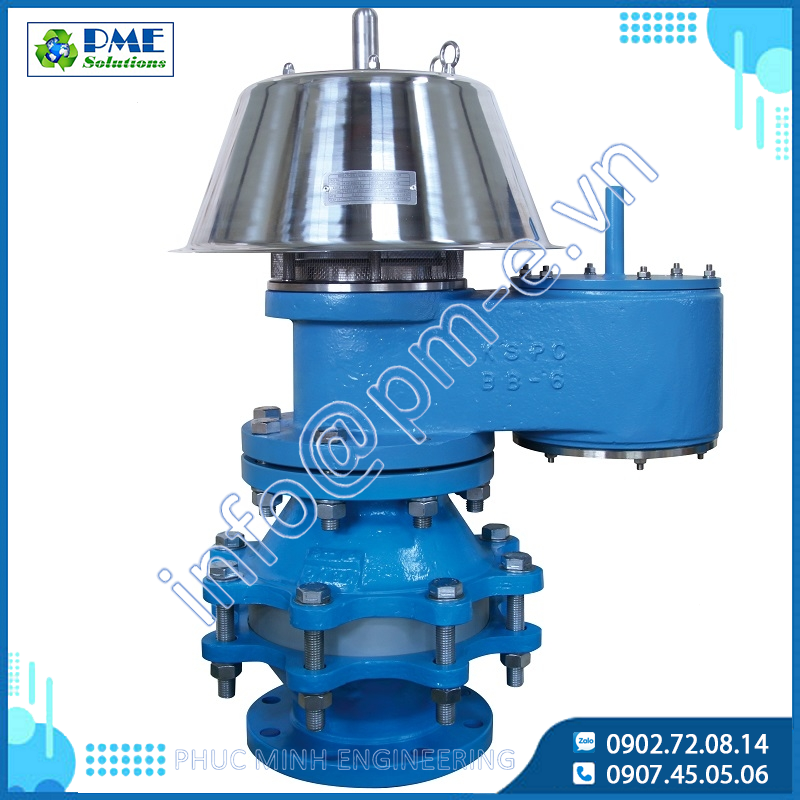
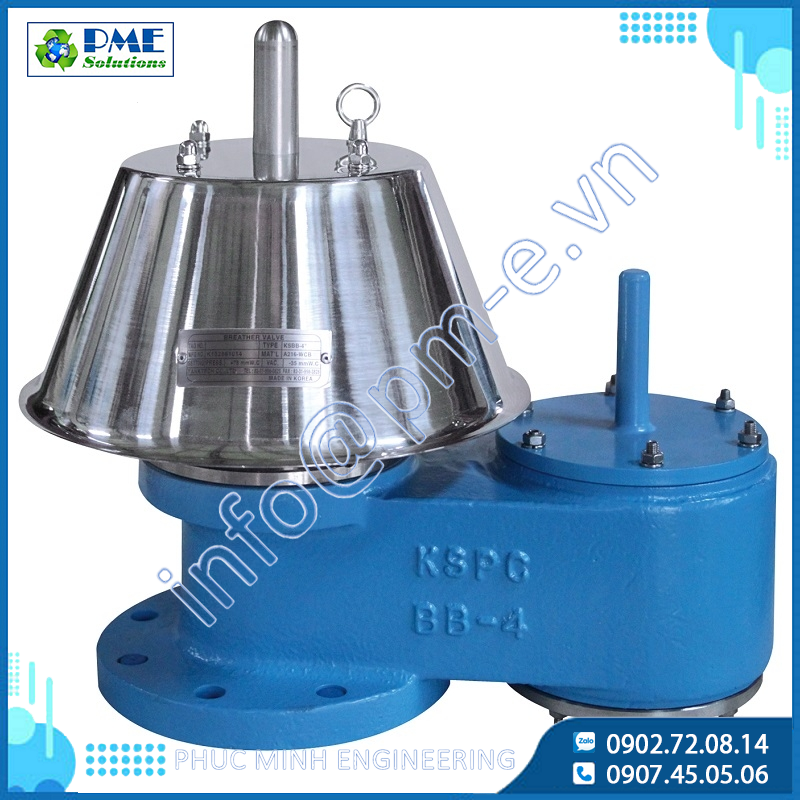
KSPC Industrial Valves and Breather Valve Solutions with Flame Arresters at Phuc Minh
17/12/2025
Learn what industrial valves are and the importance of KSPC breather valves with flame arresters. Safe installation guide and exclusive distributor Phuc Minh.

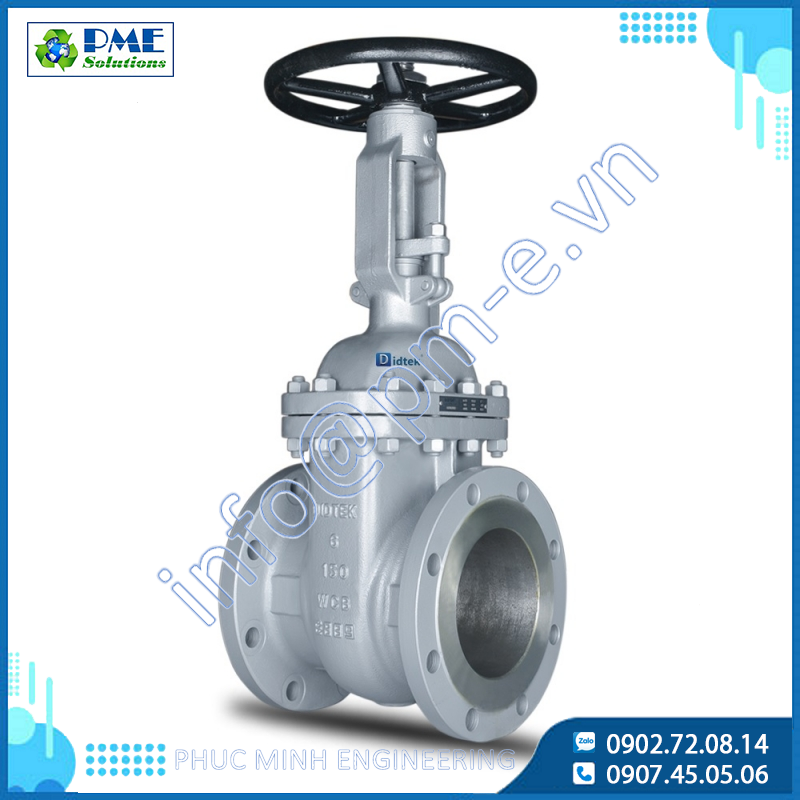
inVal Industrial Valves: Stainless Steel Gate Valve Solution for Chemicals
20/12/2025
Discover VinVal industrial valve lines, especially specialized stainless steel gate valves. Learn how to select the most effective valve for corrosive chemicals
















.png)






