Knowledge of various types of float, disc, and inverted bucket steam traps
KNOWLEDGE ABOUT STEAM TRAPS
Knowledge of various types of float, disc, and inverted bucket steam traps
In manufacturing plants, boilers, steam piping systems, and heat exchangers are often used to heat products. All of these devices are condensate is generated and this condensation needs to be taken out automatically and that is why we need to install a steam trap to condense water, gas, residue... . is discharged through the steam trap/condensate drain plug. Therefore, Steam Traps are very important in steam systems, but not all technical staff who have ever come into contact with Steam Traps understand it. If you are interested and want to have more knowledge about steam traps, then please learn about steam trap equipment according to the information below.
WHAT IS A STEAM TRAP?
Steam trap, also known as condensate drain valve: is an automatic valve used to discharge condensate, gas, and scale generated inside the steam pipeline system (condensate steam). The steam trap will ensure that the steam is always dry and not wet while also limiting the loss of steam to the outside, so in the industry, the steam trap is a very important device used for steam systems that always maintain heat. Stability, avoiding water hammer phenomenon (../goc-ky-thuat/hien-tuong-bua-nuoc-thuy-kichwater-hammer-8.html)/water hammer for steam pipelines and consumption equipment steam.
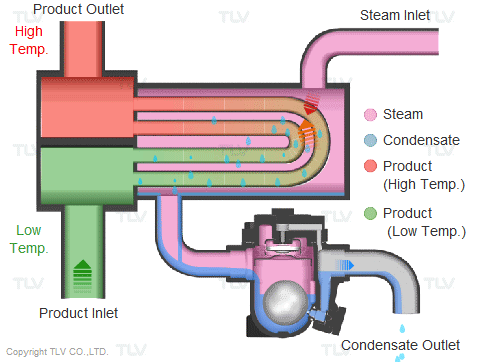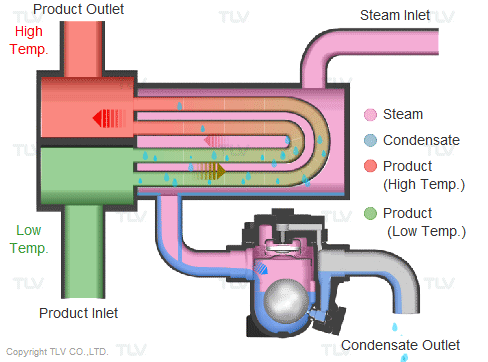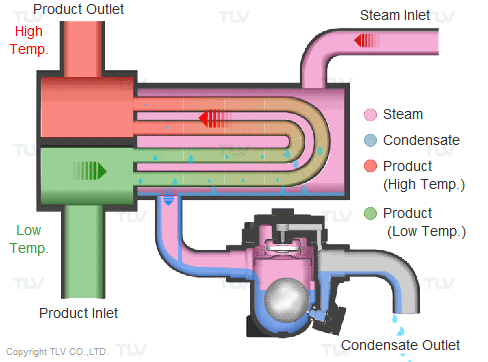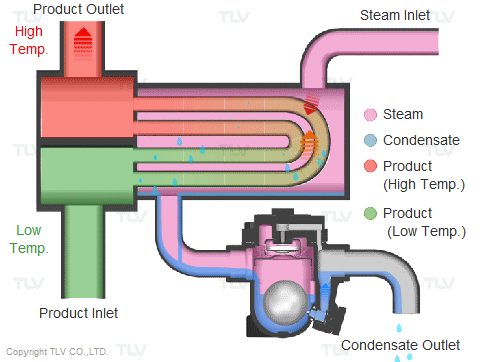

BASED ON THE STRUCTURE AND OPERATIONAL PRINCIPLES OF THE STEAM TRAP
STEAM TRAPS ARE DIVIDED INTO 3 TYPES AS FOLLOWS:

Mechanical steam trap: Works based on the difference in density between steam and condensate.
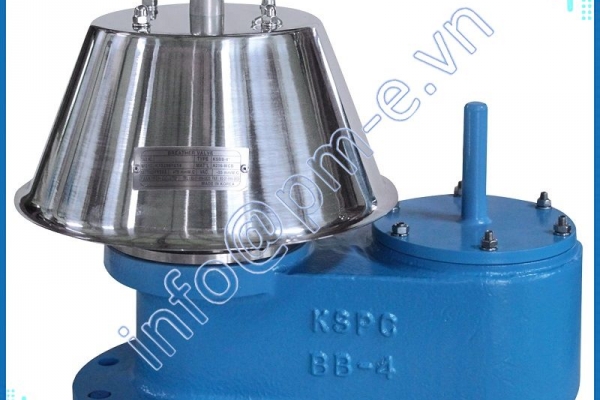
1.1 Float steam trap: Float steam trap is most commonly used in heating systems, thanks to the mechanical float mechanism that releases condensate and the thermostatic air vent mechanism when first started, both two things play an important role in the heating system.

- Operating principle: When the system starts, gas and condensate enter the steam trap. The air will be released through the thermostatic air vent. The condensate enters and lifts the float, the mechanical mechanism opens the valve to let the condensate escape. When hot steam enters the steam trap, the thermostatic expands and closes the thermostatic air vent, preventing steam from escaping. When the condensate drains out, the float lowers and causes the mechanical mechanism to close the orifice valve. When the float lowers, the mechanical mechanism closes the valve. This valve is always below the water level so the heat cannot escape. The up-and-down float causes the valve to open and close continuously at many different angles and balance the amount of condensate entering and the condensate leaving. To meet the discharge flow and balance the force of the incoming steam pressure, the internal structure of a conventional steam trap has many options for valve diameter sizes to meet the needs of discharge flow and discharge. Working pressure of steam trap.
1.2 Bucket steam trap: Bucket steam trap has a sturdy structure with the advantage of condensate on the top of the steam trap, thus limiting the risk of impurities stuck in the pipeline.


- Operating principle: Inside the bucket, when there is a lot of water, it will tend to sink below the steam trap, causing the mechanical mechanism to open the valve to let the condensate escape. Above the bucket there is a small "bleed hole" to allow air to escape from inside the bucket and then escape into the condensate system. When steam enters the steam trap, enters and raises the bucket, the mechanical mechanism closes the valve. The condensate continues to go inside the bucket and out the lower body of the steam trap. When there is a lot of condensate in the steam trap and the pressure of the steam pushing the bucket to close the valve slowly decreases because the steam slowly escapes through the small discharge hole above the bucket. After the water fills the bucket (the bucket), the bucket is broken. pushed down because of its weight and causes the valve to open and drain the condensate. After draining all the condensate, the steam enters and slowly lifts the bucket because there is a small exhaust hole above the bucket to help the steam escape and let the hot steam inside the bucket. Slowly push the valve up and close. again. The bucket steam trap must always have water in the steam trap for the bucket steam trap to operate. Otherwise, the steam trap will always be open, allowing steam to escape.


2. Thermodynamic steam trap (Disc steam trap): operates based on the dynamic properties of condensate and steam.

Thermodynamic steam trap: This is a simple, safe device that can operate at high temperature and pressure. Thermodynamic steam traps are used to discharge condensate and retain heat in the steam system. They are commonly used in places with low discharge flow, often on the main steam line and in some locations where the amount of condensate is low. The outstanding feature of thermodynamic steam traps is that they are not affected by water shock and system vibration.

Operating principle: When the steam system starts or is operating, condensate in the steam system tends to lie below the pipes and stagnate in low locations or enter steam trap stations. Steam trap stations will open to discharge condensate and close to prevent steam from escaping. The steam trap opens to discharge condensate, thanks to the high pressure (steam pressure) pushing the condensate through the other side of the steam trap (low pressure). At the time the condensate has not yet escaped through the other side of the steam trap, the water has the same temperature as the hot steam. When condensate drains through the Orifice hole, the pressure decreases, causing the boiling temperature of the water to also decrease. The condensate in the coin disk area will have excess energy and boil to produce flash vapor, the flash vapor will go out to the condensate system, a little flash vapor will rise and stagnate above the coin disk, the flash vapor will tend to push the disk. Go down and close the steam trap. When the condensate has completely escaped through the steam trap and the hot steam continues to come out, because the steam passes through the surface of the disc at a velocity many times greater than the velocity of the water, a low pressure area will be created below. disc, plus the force of the flash vapor above the disc pushing the disc down, causing the valve disc to close. Because the cross-sectional area of the disc is many times larger than the cross-sectional area of the valve discharge hole, the thrust force on the disc is greater than the force under the disc and helps the valve close after the live steam passes through the steam trap. After a certain period of time, the condensate in the steam system will continue to go down to the steam trap station, and the flash steam energy on the disk will also gradually weaken due to heat loss (due to energy being lost to the outside), Therefore, the thrust due to the pressure of the steam system will push the disc up and drain the condensate out the outlet of the steam trap, and this process repeats throughout the operation of the steam trap. When the amount of condensate in the system is low, and now only live steam enters the steam trap, at that time, the steam trap will open/close/open/close/ continuously to release live steam out and not unavoidable throughout the operating cycle of this type of disc steam trap. Because the amount of steam that closes the disc can only be held for a short period of time, depending on the speed of heat loss above the disc, such as when the weather is rainy or during the cold air season outside the trap. The heat loss above the trap is rapid and the number of opening and closing times also increases. Conversely, if the weather is hot, the steam trap is well insulated, or the steam trap has an insulation layer made of live steam or air inside the trap. This is an ideal insulation layer that helps reduce heat loss above the trap and helps the valve stay closed longer, reducing the amount of steam escaping.



Phuc Minh Engineering Company specializes in consulting and distributing steam traps with the latest technology and highest quality, helping to save steam energy for customers when coming to us. Our steam traps are distributed from TLV, Yoshitake to Venn, Samyang, Gastra, Spirax Sarco, VYC, ADCA, Hydroproduct, SteamPro, Nicosson, Tunglung, Taiwan, China,... from the lines of Disc Steam Traps, Steam Traps. float steam trap, bucket steam trap, thermostatic steam trap, orifice steam trap,...
If you need detailed advice, please contact us via: 0902800728 meet Mr.Vinh ( vinh@pm-e.vn ) or 0907450506 meet Mr. Duong ( duong@pm-e.vn ) or 0902601875 Meet Mr. Thanh ( thanh@pm-e.vn )
Very pleased to serve you!





















.png)






